Guide for Reviewers
Reviewer Process
• Articles submitted to TAY Journal are evaluated by at least two referees using the principle of blind refereeing (double-blinding method).
• Reviewers are selected from among experts on the topic addressed in the candidate article.
• The selected reviewer is informed about the responsibilities of TAY Journal reviewers and the ethical principles to be followed, article evaluation criteria and procedure.
• The reviewer should inform the editor within fifteen (15) days whether or not can evaluate the candidate article, taking into account the evaluation period stipulated for the candidate article and the suitability of the subject of the candidate article.
• At the end of this period, the referee who has not made a decision is deemed to have rejected the evaluation and the editor will appoint a new reviewer.
• The reviewer who accepts the evaluation is given 30 days to evaluate the candidate article.
• If the reviewer can not evaluate the candidate article within the time limit, he/she may request additional time from the editor or inform the editor that he/she cannot evaluate the candidate article due to time constraints. In this way, the author can be prevented from losing time and the editor will be given enough time to appoint a new reviewer.
• If the candidate article receives two rejections or one rejection and one major revision at the end of the referee reports, the author(s) will be notified that it is not accepted for publication with the reasons. In other cases, the chief editor/editors may review the reviewer report and initiate an additional evaluation process if necessary.
Transparency Principle
At TAY Journal, all correspondence between authors and editors, as well as editorial, editorial board and peer review processes are transparent.
Privacy Principle
The names of the authors are not mentioned in the articles sent to the reviewers and the names of the reviewers are not mentioned in the reports sent to the authors. However, in order to make a better academic contribution to the author, the editor may ask the reviewers to make suggestions to each other's reports. In this case, the names of the reviewers are not disclosed to each other.
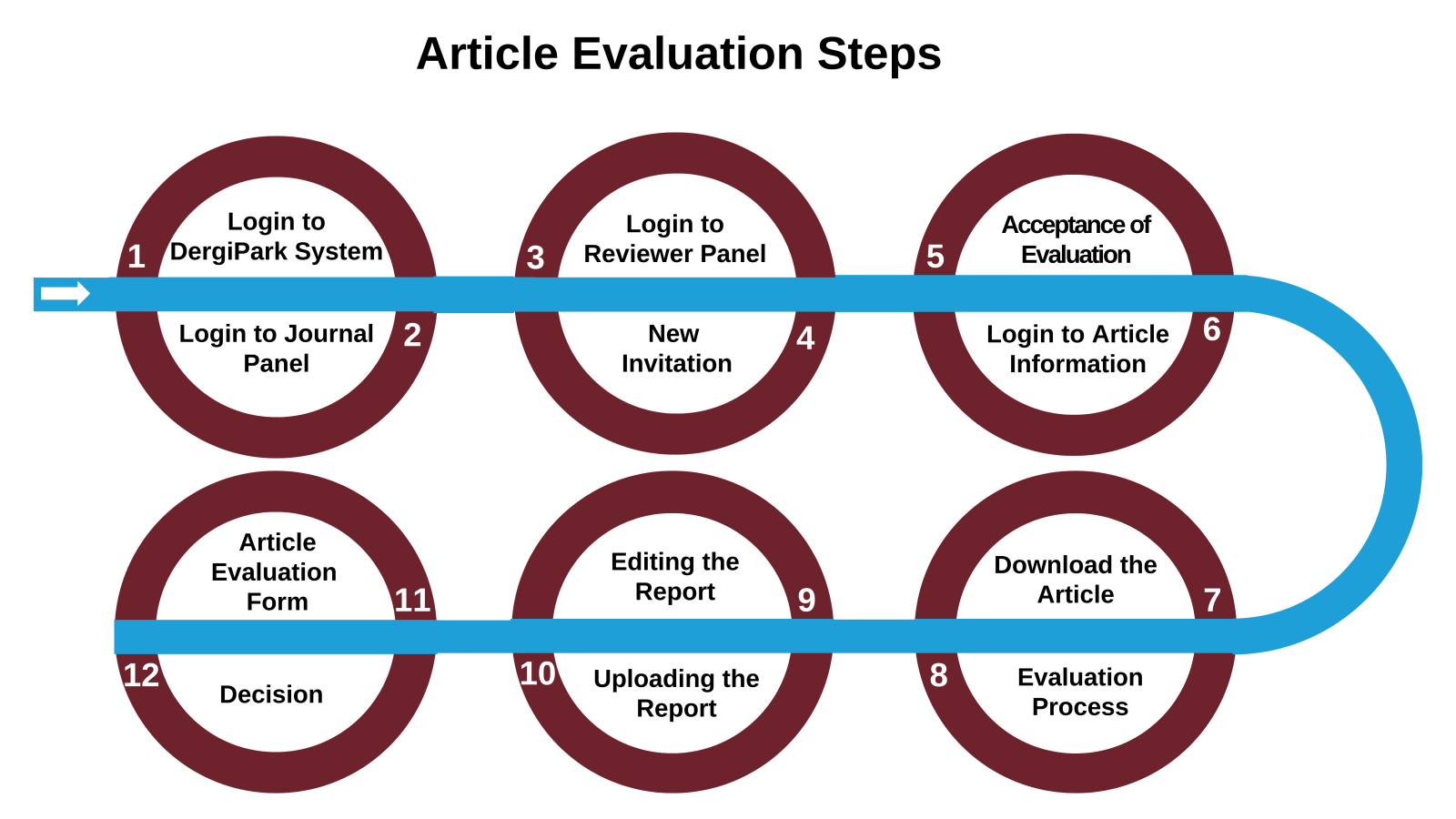
Article Evaluation Steps
The steps that TAY Journal reviewers should follow to evaluate the article submitted from the system are as follows:
1. Login to the DergiPark system with your username and password.
2. Log in to TAY Journal's Journal Panel from My Journals section.
3. Log in to the reviewer panel.
4. From the “New Invitation” tab, click on the title of the article you are assigned as a reviewer.
5. On the page that opens, you are asked whether you agree to evaluate the article. To accept, click on the “Accept Evaluation” button in the green section.
6. Click on the “Show” button on the right of the relevant article to access the article information.
7. Click on the “Files” tab and download the article by clicking on the “Download” icon to the right of the article under the “Article Files” heading.
8. Record your evaluation notes on the article. To do this, you need to click on the “Review” tab in the Word document and activate the “Track Changes” button. If necessary, you can add a comment using the “New Explanation” button or the menu that appears when you select the relevant text and right-click. While making your evaluations, it is important that you take into account the criteria in the “Article Evaluation Form” and make your comments within this framework.
9. After completing your evaluation, change the file name to “ Reviewer's Report". Then delete the referee information from the file. This is important to prevent the author from accessing the referee information (“File-Information-Check Issues-Review Document-Check-Document Properties and Personal Information-Remove All” or “Tools-Protect Document-Privacy-Recorders-Personal Information-Remove from This File”).
10. After logging in to the relevant article from the panel, go to the “Files” tab and upload your report using the “Add New File” button.
11. In the article panel, click on the “Evaluation” tab, fill in all the fields in the “Article Evaluation Form” at the bottom of the page and complete the process by clicking the “Submit Evaluation” button. After this process, you should see the message “Your process has been completed successfully” at the top of the page.
12. You can make the following decisions under the “Recommendation” heading at the end of the form:
• Major Revision
• Minör Revision
• Reject
• Accept
Article Evaluation Criteria
TAY Journal expects the reviewers to evaluate the candidate article by taking into account the following points:
1. The appropriateness of the article subject to the scope of the journal's subject area
2. The compatibility of the title and subheadings with the subject of the article
3. Adequacy of the abstract to reflect the article
4. Relevance of keywords to the article subject
5. Adequacy of literature review
6. Systematic presentation of the article topic within the framework of the literature
7. Adequate explanation of the reasons and problem of the article
8. Clear expression of the aims and problems of the article
9. Appropriateness of the method used
10. Correct application of the method
11. Sufficiency of information on the selection and characteristics of the data source
12. Adequacy of information on data collection tools
13. Adequacy of knowledge about the data collection and analysis process
14. Relevance of findings to research problems
15. Presentation of the findings accurately and clearly in accordance with the methodology
16. Discussing the research results within the framework of the literature in accordance with the research problems
17. Relevance of the recommendations to the findings of the article
18. Indication of limitations of the research
19. Relation of the cause and effect relationships established in the conclusion, discussion and recommendations sections with the findings and literature
20. Access to original and up-to-date sources
21. Compliance of in-text citations with scientific usage
22. Accuracy of writing references
23. Accuracy of the use of concepts and terms related to the field
24. Adequacy of the language and expression used
25. Originality and currency of the article
26. Contribution of the article to the knowledge in the related field
27. Compliance of the article with scientific ethics
Ethical Responsibilities of Reviewers
The ethical responsibilities of TAY Journal reviewers include responsibilities related to “confidentiality, impartiality, constructiveness, contribution to editorial decision, conflict of interest, time”. Detailed information on these issues can be found in the relevant section of the Ethical Principles and Publication Policy.
Feedback to Reviewers
According to the reviewers' recommendations, the editor/editorial board follows one of the following paths:
• Accept the manuscript for publication with a request for minor or major revision.
• It may ask the author(s) to edit the manuscript in accordance with the reviewer's comments and initiate a new evaluation process.
• Reject the manuscript.
In their reports, the referees can give a definite opinion on whether the study should be published or not. However, the editor will make a decision based on the opposing views of the reviewers. The editor may not look at the number of reviewers who accepted or rejected the manuscript and may make a decision based on the strength of the reviewers' or authors' arguments. The editor considers reports with strong, well-reasoned propositions rather than reports with yes or no answers to the evaluation questions.
The final version of an article that has been decided to be published is sent only to the reviewer who wishes to see the manuscript again. After an article is published, the referee may find that his or her own views are not fully reflected in the article. It is possible that other reviewers may have different opinions and the editor may have taken these opinions into consideration. In this case, the opinions of other referees can be sent to the reviewer upon the request of the referee who evaluated the work.
Read 3.225 times.